
Depreciation of some fixed assets can be done on an accelerated basis. Merriam-Webster provides some accelerate synonyms that include "quickened" and "hastened." A larger portion of the asset’s value is expensed in the early years of the asset’s life. Some examples difference between accumulated depreciation and depreciation expense of fixed or tangible assets that are commonly depreciated include buildings, equipment, office furniture, vehicles, and machinery. Running a business is no small feat and companies need both tangible and intangible assets to operate and drive profitability.
What to know about Form 4562: Depreciation and Amortization
The difference between the end-of-year PP&E and the end-of-year accumulated depreciation is $2.4 million, which is the total book value of those assets. While accumulated depreciation is reported in the balance sheet, depreciation expense is reported in the income statement. Accumulated depreciation is used in calculating an asset’s net book value. Net book value is the cost of an asset subtracted by its accumulated depreciation.
What Is the Basic Formula for Calculating Accumulated Depreciation?
Companies may do this so they can claim higher depreciation deductions on their tax returns and because it stretches the difference between revenue and liabilities. More depreciation expense is recognized earlier in an asset’s useful life when a company accelerates it. Looking for a comprehensive fixed asset and depreciation accounting software? Thomson Reuters Fixed Assets CS has the tools to help firms meet all of a client’s asset management needs. It also helps with asset valuation, enabling clients to more accurately report an asset at its net book value. For example, say Poochie’s Mobile Pet Grooming purchases a new mobile grooming van.
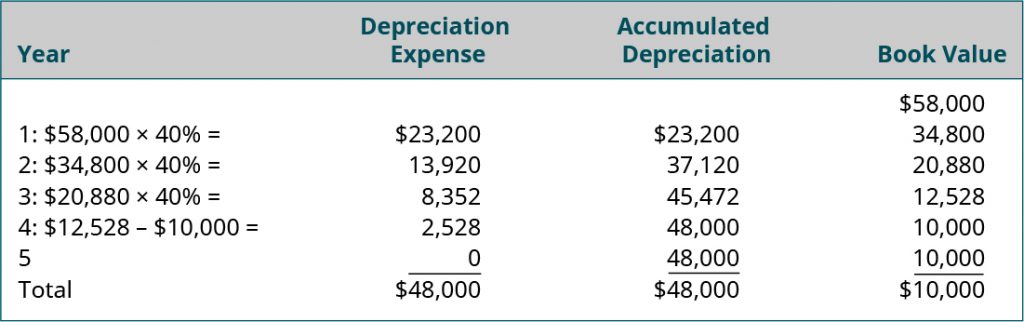
Accumulated Depreciation, Carrying Value, and Salvage Value
- It is in this sense that depreciation is considered a normal business expense and, consequently, treated in the books of account in more or less the same way as any other expense.
- It appears on the balance sheet as a reduction from the gross amount of fixed assets reported.
- Proration reduces the depreciation that you can claim in a given year.
- Assets that are expensed using the amortization method typically don’t have any resale or salvage value.
Instead, the cost is placed as an asset onto the balance sheet and that value is steadily reduced over the useful life of the asset. This happens because of the matching principle from GAAP, which says expenses are recorded in the same accounting period as the revenue that is earned as a result of those expenses. Accumulated Depreciation is a contra-asset account that represents the total amount of depreciation expense recorded over the life of an asset. Its purpose is to provide a clear picture of the asset’s net book value, which is essential for accurate financial reporting.
Expected Useful Life and Salvage Value
You can account for this by weighting depreciation towards the initial years of use. Declining and double declining methods for calculating accumulated depreciation perform this function. The double declining method accounts for depreciation twice as quickly as the declining method. Here are some scenarios where accelerated depreciation accounting methods might be the right choice.
Reporting in the books of accounts
In layman’s language, it increases the expense section on an income statement, while decreasing the retained earnings. In simple words, its balance begins at zero every accounting period, and is then closed to an equity account (typically, retained earnings) at the period’s end. To be more precise, accumulated depreciation and depreciation expense help us observe how a business uses and values its resources. More importantly, this is vital information for everyone involved, from the investor to the business manager.
Depreciation expense is recognized on the income statement as a non-cash expense that reduces the company’s net income. For accounting purposes, the depreciation expense is debited, and the accumulated depreciation is credited. The accumulated depreciation account is a contra asset account on a company’s balance sheet, meaning it has a credit balance. It appears on the balance sheet as a reduction from the gross amount of fixed assets reported. On the other hand, depreciation expenses represent the assigned portion of a company’s fixed assets cost for a specific period. These expenses are recognized on the income statement as non-cash expenses that reduce the company’s net income or profit.
Our intuitive software automates the busywork with powerful tools and features designed to help you simplify your financial management and make informed business decisions. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. 11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas.
